Forspell
Forspell is a spellchecker for code and documentation. It uses the well-known hunspell tool and dictionary, provides customizable output, and could be easily integrated into CI pipeline.
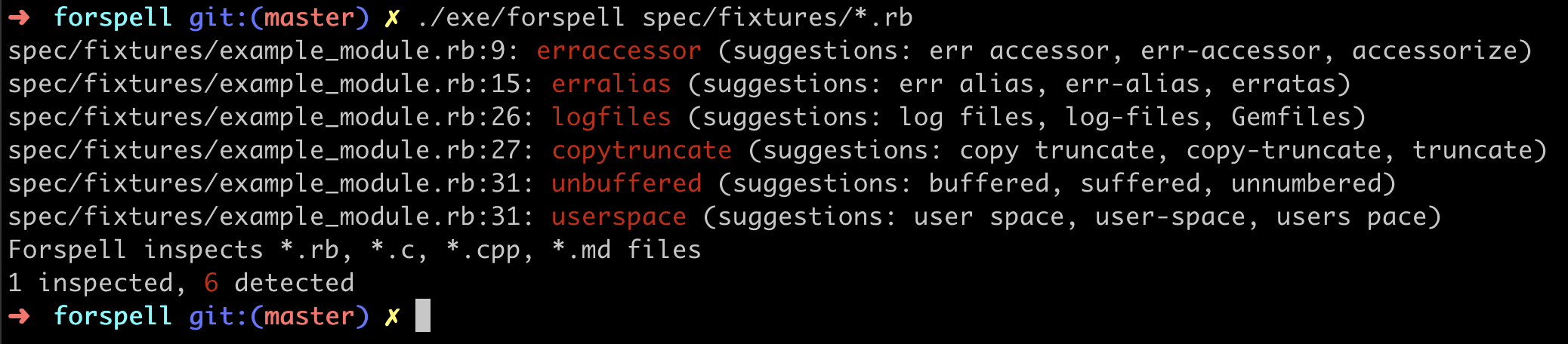
Here's an output example:
Features
- Ability to check Markdown files and comments in Ruby, C and C++ code;
- Skipping over code examples and identifiers inside comments and Markdown most of the time;
- Distributed with latest en-US hunspell dictionaries, but can be set to use any other dictionary;
- Includes a custom Ruby ecosystem-related dictionary (so it will not report words like "Gemfile", "args", "middleware" and alike as misspelled);
- Easiness to create a custom dictionary for your project, so your internal terms would not be reported as misspellings;
- Option to auto-generate initial custom dictionary;
- Several output formats, including pretty print, YAML and JSON.
Installation
gem install forspell
forspell requires libhunspell >= 1.2.0 to be installed, see hunspell site for installation instructions (it is probably as easy as <yourpackagemanager> install hunspell on most of *nix and MacOS).
Usage
$ forspell --help
Usage: forspell [list of files and folders] [options]
Options:
-e, --exclude paths List of paths to exclude
-d, --dictionary path Path to main hunspell dictionary to use (by default, forspell's en_US)
-c, --custom paths Paths to custom dictionaries
-f, --format format_name Output formats: readable (default), json, yaml
--gen-dictionary Generate custom dictionary
-l, --logfile path Log to specified path
-v, --verbose Verbose mode
--help
forspell automatically loads command-line arguments from .forspell file in current folder, if it is present.
Arguments for forspell command are directories or separate files you want to check.
With no arguments provided, a current directory will be processed.
Supported file extensions are .rb, .c, .cpp, .md.
Dictionaries
Forspell uses hunspell dictionaries to check spelling. By default, it is the en_US modern dictionary, distributed with forspell itself, but you can specify any other with -d option. If you have /some/custom/path/fr_FR.aff and /some/custom/path/fr_FR.dic, than you can use it instead of en_US with -d /some/custom/path/fr_FR.
In addition to the main dictionary, forspell also includes (and always uses) small auxiliary dictionary with words specific for Ruby ecosystem, you can review it in forspell repo.
You can also add your project's custom dictionary with internal terms, for them not to obstruct spellchecker's output. Custom dictionary (or several) may be passed with -c option. Also, forspell.dict will be automatically processed, if presented in current directory. Format of custom dictionary:
- Each word on its own line.
- Line contains either just
word(means only this word in this form). - ...or
word: example-- in this case, "example" should be existing word from the main dictionary, and it means your custom term can have the same forms as example word. For example, "subclass: class" will mean that "subclass", "subclasses" and "subclass'" should be considered correct. -
#marks comments.
For larger projects, it is handy to generate a custom dictionary with forspell your,project,paths --gen-dictionary. This will create forspell.dict with all misspellings found in your project, and you can proceed by deleting genuine errors and leave internal terms, which should be considered correct.
Integration with CI
Forspell's return codes:
- 0 - when no errors found
- 1 - when there are any errors
- 2 - when it could not process with provided options, i.e. no dictionary found, no directories for checking supplied.
To integrate forspell with, say, TravisCI, you would add to .travis.yml:
-
sudo apt-get install hunspellintobefore_installsection - Just
forspellintoscriptsection (given you have proper.forspellfile with all options what to check and how to output)
Authors
License
MIT
Contributing
Feel free to create an issue or open a pull request!