TDI
Test Driven Infrastructure acceptance helpers.
Validate your deployed infrastructure and external dependencies.
Installation
Add this line to your Gemfile:
gem 'tdi'And then execute:
$ bundleOr install with:
$ gem install tdiUsage
$ tdi [-h]
Usage:
tdi test_plan_file [options]
Examples:
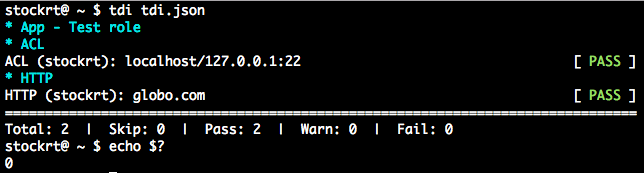
tdi tdi.json
tdi tdi.json -n
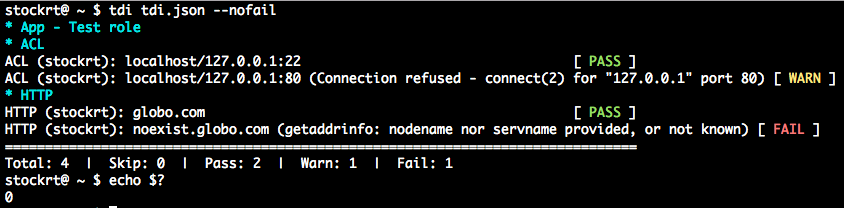
tdi tdi.json --nofail
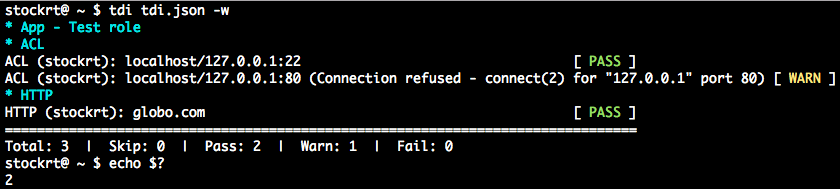
tdi tdi.json -w
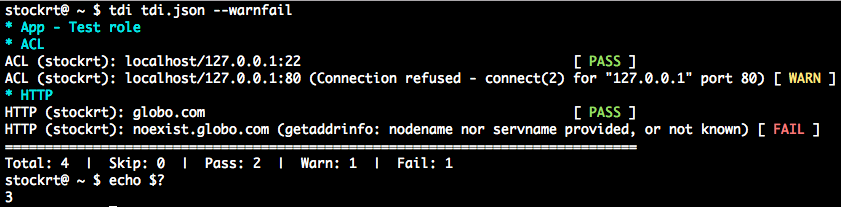
tdi tdi.json --warnfail
tdi tdi.json -p app
tdi tdi.json --plan app
tdi tdi.json --plan app::acl
tdi tdi.json --plan app::acl,app::file
tdi tdi.json -r /tmp/tdi-report.json
tdi tdi.json --reportfile /tmp/tdi-report.json
tdi tdi.json -s
tdi tdi.json --shred
tdi tdi.json -v
tdi tdi.json -vv
tdi tdi.json -vvv
tdi --version
Options:
-n, --nofail No fail mode.
-w, --warnfail Fail if any warning.
-p, --plan Test plan list.
-r, --reportfile Report file to save test plan status.
-s, --shred Wipe out the test plan, leaving no trace behind.
-v, --verbose Verbose mode.
--version Version.
-h, --help Display this help message.Test plan samples
ACL
Test network access/filters for TCP services.
{
"app": {
"desc": "Test role",
"acl": {
"port": 80,
"www.globo.com": {},
"globoesporte.globo.com": {},
"cartolafc.globo.com": {},
"doesnotexist.globo.com": {},
"www.example.com": {
"port": [80, 9999],
"timeout": 3
},
"localhost": {
"port": [22, 31337]
}
}
}
}FILE
Test files and diretories permissions.
{
"app": {
"desc": "Test role",
"file": {
"user": "nobody",
"perm": "rw",
"type": "file",
"location": "local",
"/tmp/afile1.txt": {},
"/tmp/afile2.txt": {
"perm": "ro"
},
"/tmp/afile3.txt": {
"user": "root"
},
"/tmp/doesnotexist/afile.txt": {},
"/tmp/doesnotexist": {
"type": "directory"
},
"/tmp": {
"type": "directory"
}
}
}
}HTTP
Test URLs and match expected responses.
{
"app": {
"desc": "Test role",
"http": {
"globoesporte.globo.com": {
"match": "<html"
},
"http://globoesporte.com": {
"code": 301,
"expect_header": "Location: http://globoesporte.globo.com/"
},
"http://api.sde.globo.com/docs": {
"code" : 301
},
"https://api.sde.globo.com/path/to/resource": {
"code" : 401
},
"doesnotexist.globo.com": {},
"https://api.cartola.globo.com/mercado/status.json": {},
"https://api.cartola.globo.com/wrong-url": {},
"http://g1.globo.com": {
"code": 301,
"match": "<html"
},
"http://g1.globo.com/index.html": {
"match": "<html"
}
}
}
}SSH
Test SSH access and login using public/private key pairs.
{
"app": {
"desc": "Test role",
"ssh": {
"timeout": 7,
"u_remote@localhost": {
"local_user": "u_local"
},
"u_remote2@localhost": {
"local_user": ["u_local", "u_local2"]
}
}
}
}Generating test plans
You may write your test plans as JSON in the following ways:
-
By hand, as pure JSON files
-
Using some templating engine (ERB, Jinja, etc...)
-
With your favorite programming language (Ruby, Python, etc...)
It does not matter how you generate your test plan, as long as it results in a valid JSON file. Certainly it would be a good idea to write your test plans from within Capistrano/Fabric/Chef/Puppet. Since the difference between environments (development, staging, production) should be known by your deployment tool, it would be clever to let that tool decide which paths, users, permissions and addresses to write into the test plan file.
Bellow we give you some suggestions on how to generate your test plans more efficiently (because writting JSON by hand is boring):
Ruby
require 'json'
tdi_plan = {
:app => {
:desc => 'Test role',
:acl => {'localhost' => {:port => [22, 80]}},
:http => {
'globo.com' => {:code => 301},
'noexist.globo.com' => {:code => 200},
},
}
}
File.open('tdi.json', 'w').write(JSON.pretty_generate(tdi_plan))Python
import json
tdi_plan = {
'app': {
'desc': 'Test role',
'acl': {'localhost': {'port': [22, 80]}},
'http': {
'globo.com': {'code': 301},
'noexist.globo.com': {'code': 200},
},
}
}
open('tdi.json', 'w').write(json.dumps(tdi_plan, indent=2))Validating your plan file
Use JSONLint site to validate your JSONs.
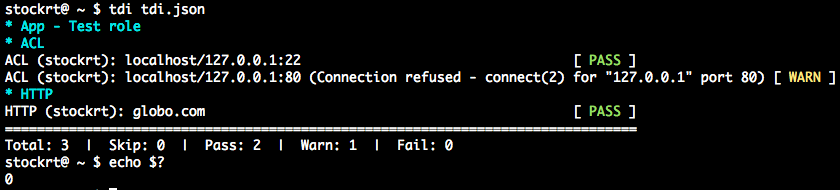
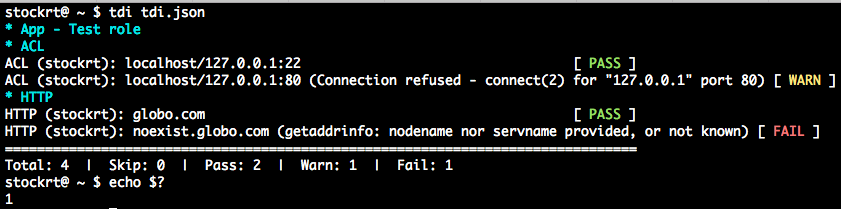
Running test plans and their possible return codes
Return codes are:
-
0if allsuccess
-
0by default even if warning (warning should not generate a validation error)
-
1if anyfailure
-
2if anywarningplus option-wor--warnfail
-
3if bothfailureandwarningplus option-wor--warnfail
-
0regardless failure or warning if-nor--nofail